Google Algorithm Updates
There are a number of algorithm update logs available online.
We don't aim to be the most comprehensive, but rather to highlight some of the more important changes in terms of their impact on the field of SEO. The biggest & most impactful updates (like Florida, Panda & Penguin) are bolded.
Current Google SERP volatility is shown in the following widget from SEMrush.
Year by Year Index of Historical Google Updates
2003 2005 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025
How Algorithm Updates Work
Google launches hundreds to thousands of minor algorithm updates each year. Larger updates happen roughly every other month to quarterly. The aim of most smaller updates is to improve specific features and relevancy matching while having limited potential adverse impact on the seach ecosystem as a whole. Larger updates have far more widespread impacts and can have flux which lasts for weeks as search engineers adjust ranking factors in part based on feedback from end users and publishers about the algorithm update.
As the web changes publishing strategies and monetization strategies change. Google tries to improve user experience by delivering precisely what they believe the user is searching for. In many cases that means showing a featured snippet, a knowledge box with information about an entity, or a vertical search result above the traditional 10 blue links. If and when Google sends users to third party websites they want to ensure those websites also deliver a clean user experience where solutions are easy to find.
As the web changes Google search engineers update their search quality evaluator guidelines [PDF] which are used by thousands of freelance workers to grade how well Google is doing in terms of delivering a quality search experience.
The following video by Google search engineer Paul Haahr describes what his job is like and how they measure ranking success.
2003
November 16th: the Florida Update was when SEO first got complex enough to where many people started needing the help of external experts. Before this update one could easily rank well by buying lots of links using the anchor text they wanted to rank for & repeating a keyword on the page. This is the update that introduced nuance into SEO. Google rolled out this huge update while they were still powering Yahoo! Search & before Yahoo! switched to their own in-house search algorithm.
2005
- January 18th: Nofollow launched to allegedly curtail comment spam. Google would later shift the purpose of this tag from fighting blog comment spam to something which should be required on any paid links. After about 15 years Google later changed their policies stating they may count some nofollow links for rankings as they would treat nofollow as a hint rather than a directive. They also announced rel="ugc" & rel="sponsored" when they announced the change to rel="nofollow" would go into effect on March 1, 2020.
- June 28th: Search personalization features added so websites you visit regularly may be ranked higher in the search results. Later on Google would further enhance personalization by increasingly localizing the search results, both within a particular country and down to the city level. In 2014 Google even started going more granular like down to the neighborhood level in some larger cities. As online news ad budgets crumbled newspapers became more partisan to maintain audience by feeding a constant drip of confirmation bias to readers. This economic shift in news creation along with social networks that amplified outrage caused the rise of what Eli Pariser's book The Filter Bubble, Donald Trump getting elected as president of the United States, and savvy marketing by DuckDuckGo forced Google to dial back on personalization of the search results outside of localization.
2007
May 16th: Google rolls out Universal Search which mixes YouTube, news & other vertical search types into their core index. Later they add their knowledge graph and a variety of paid-only verticals in areas like hotel search, flight search, financial products, product/shopping search. Some verticals change over time to include free tiers (shopping search, flights search) or are retired (financial offers).
2008
August 25th: Google Suggest auto-completes user search queries after they start typing their search query, which attempts to drive them down well worn paths, further minimizing traffic sent to misspellings and some lesser searched for longtail phrases.
2009
February 20th: The Vince Update is where we started the whole "brand, brand, brand" stuff. This happened *after* the financial crisis, when Google's revenue growth stagnated & Google share prices plunged. March of 2009 was the bottom of the stock market plunge, when congress pushed FASB to allow for widespread accounting games by relaxing mark-to-market requirements. By promoting brands Google achieved a number of key objectives:
- took much of the risk out of result rankings
- defunded a lot of independent SEO-only or excessively SEO-focused publishing efforts
- shortened the information supply chain
- consolidated ad spend back toward Google
- increased the perceived importance of the search channel (paid and organic) to large brand advertisers
- increased the awareness of already popular brands & gave them extra incentive to bid on their branded keywords (even though the economics of bidding on their own brand typically did not make sense for advertisers as it cannibalized their organic search clicks & taking advantage of selection effect)
It’s plain to see that junior’s no marketing whiz. Pizzerias do not attract more customers by giving coupons to people already planning to order a quattro stagioni five minutes from now. Economists refer to this as a "selection effect." It is crucial for advertisers to distinguish such a selection effect (people see your ad, but were already going to click, buy, register, or download) from the advertising effect (people see your ad, and that’s why they start clicking, buying, registering, downloading). Tadelis asked how exactly the consultants made this distinction.
When you bid on your own brand, you are frequently paying to capture an audience you would have already reached without spending that money.
Brand keyword advertising, the presentation informed him, was eBay’s most successful advertising method. Somebody googles "eBay" and for a fee, Google places a link to eBay at the top of the search results. ... Three months later, the results were clear: all the traffic that had previously come from paid links was now coming in through ordinary links. Tadelis had been right all along. Annually, eBay was burning a good $20m on ads targeting the keyword ‘eBay’.
Microsoft - which owns the Bing search engine - also did a study showing most brand-bidding on your own brand wastes money.
At Microsoft, Rao had a search engine at his disposal: Bing. Following the news about the millions of dollars eBay had wasted, brand keyword advertising only declined by 10%. The vast majority of businesses proved hell-bent on throwing away their money.
If brand bidding offers such a horrible ROI why do so many advertisers still do it? Largely for job preservation of the internal marketing team and external markeitng consultants. Anyone who looks at the data without understanding selection effect will think the numbers are better than they are. Plus if the consultant gets a percent of spend and has required ROI metrics to meet then ignoring the brand cannibalization makes the numbers look better than they are with little to no effort AND allows them to increase ad spend on other keywords by using the phantom profits to meet an overall ROI goal.
He graciously admitted that he either added or omitted data to his model if it led to the ‘wrong’ results. Lewis: "I was like: oh man. All of that is bad scientific practice, but it’s actually great job preservation practice.
2010
September 8th: Google Instant turned Google suggest the default search behavior. On July 26, 2017 Google turned off this feature, but in the 7 years it existed it helped consolidate search query volumes into tighter buckets which users still rely on as they type, particularly on mobile devices.
2011
- February 24th: Panda Update 1.0 impacted 12% of queries, US & English only.
- April 11th: Panda Update 2.0 (about 7 weeks later) impacted about 2% of queries, incorporated user block signal, hit eHow & was rolled out internationally in the English language.
- May 10th: Panda Update 2.1 (about 4 weeks later)
- June 16th: Panda Update 2.2 (about 5 weeks later) allegedly improved scraper detection (though Google has still asked for help on this front)
- July 23rd: Panda Update 2.3 (about 5 weeks later)
- Google analytics changes (that further obfuscated some data)
- July 28th - Google blended image traffic in core search traffic by default. Previously they were seen as separate traffic sources.
- August 11th - changed session handling, which increased visit counts while offsetting that with lowering time on site metrics, higher bounce rates, and such.
- Google analytics changes (that further obfuscated some data)
- August 12th: Panda Update 2.4 (about 3 weeks later) rolled out to foreign languages with the exception of Chinese, Japanese, and Korean. impacted 6% to 9% of search queries.
- August 24th: (about 2 weeks later) not an official update, but a number of folks here that were using the subdomain work-around to get out of Panda saw their sites whacked on the 24th.
- September 28th: Panda Update 2.5 (about 10 weeks since August 12 update)
- This was the first Panda update where Google issued a weather report for future updates. Notes on this update:
- some sites that were hit saw improvements, some sites that had recovered (like Daniweb.com) were once again re-hit.
- using subdomains, HubPages had recovered over 100% of their Panda-related traffic loses.
- YouTube was yet again another big winner.
- This was the first Panda update where Google issued a weather report for future updates. Notes on this update:
- October 4th: flux on Panda 2.5.1. After publicly complaining about being hit again Daniweb recovered once again (along with some other large sites), showing how responsive Google is to public relations issues.
- October 13th: Panda 2.5.2
- October 18th & 19th: Panda 2.5.3
- November 11th: Panda 2.6/3.0
- December 13th: Panda 3.1
- December 19th: a smaller / minor Panda 3.2 update
2012
- January 16th & 22nd: Panda 3.2, which was claimed to be folding data in rather than an algorithm update
- January 19th: Ad Heavy Update
- March 23rd: Panda 3.4
- April 19th: Panda 3.5
- April 24th: Penguin update penalized aggressive low-quality link building. They also rolled out an on-page spam classifier to further obfuscate the update. Further, notice how Panda updates were included tightly on either side of this to make the weekly "what changed" SEO services have many changes appear all at once so that it is harder to isolate variables & impacts.
- April 27th: Panda 3.6
- May 16th: Knowledge graph implemented. Google begins to re-represent the world's knowledge by hosting it directly rather than indexing content and sending traffic elsewhere.
- May 25th: Penguin 2 / 1.1
- June 8th: Panda 3.7
- June 25th: Panda 3.8
- July 17th: Japanese & Korean Panda update
- July 24th: Panda 3.9
- August 20th: Panda 3.91
- September 18th: Panda 3.92
- September 27th - October 3rd: Panda 4.0 / 20 impacted 2.4% of search queries
- September 28th & 29th: EMD update lowered the rankings of exact match domain names
- October 5th: Penguin 3
- October 9th: Ad Heavy Update 2 penalized sites with a heavy ad load
- November 5th: Panda 21
- November 17th: Stealth update which hit MetaFilter and a number of other sites. The MetaFilter penalty was allegedly a false positive, but it went uncorrected for over a year, causing mental health issues & forced the founder to step away from the business.
[Google's Matt] Cutts said, “Oh yeah, I think you’re ensnared in this update. I see a couple weird things. But sit tight, and in a month or two we’ll re-index you and everything will be fine.” Then like an idiot, I made some changes but just waited and waited. I didn’t want to bother him because he’s kind of a famous person to me and I didn’t want to waste his time. At the time Google paid someone to answer his email. Crazy, right? He just got thousands and thousands of messages a day. I kept waiting. For a year and a half, I waited. The revenues kept trickling down. It was this long terrible process, losing half overnight but then also roughly 3% a month for a year and a half after. It got to the point where we couldn’t pay our bills. That’s when I reached out again to Matt Cutts, “Things never got better.” He was like, “What, really? I’m sorry.” He looked into it and was like, “Oh yeah, it never reversed. It should have. You were accidentally put in the bad pile.”
- November 21st: Panda 22
- December 21st: Panda 23
2013
- January 22: Panda 24
- January 23: Image Search interface update
- March 15th: Panda 25 is out & Google says they are unlikely to confirm or announce any further Panda updates.
- May 5th to 7th: unannounced Panda 25.1
- May 9th: Phantom/Quality update 1
- May 22nd: Penguin 4 / 2.0 impacted 2.3% of queries
- June 11th: Spammy Query Update
- June 26th & July 1st: Unnamed Authority Boosts. Google dialed up the weighting on some signals aligned with domain authority (or, conversely, they dialed down the weighting they place on raw matching relevancy). On July 9th they dialed it back slightly.
- July 16th - 18th: Panda 26 update makes Panda more granular
- July 29th & 30th: Mobile searches showing as direct visits largely fixed. Google started showing a lot of mobile searches as keyword (not provided) where they were showing up as direct website visits in the past. This was the leading edge of a multi-month campaign of Google's where they hid about an additional 1% daily of search traffic, ultimately driving the not provided percent from under half to about 90% in about 2 months.
- August 21st & 22nd: Unannounced update
- Aughst 26th to September 4th: Hummingbird update extended Google's scrape-n-displace efforts. This update rolled out in phases over time.
- September 3rd & 4th: Wave of manual link penalties
- October 4th: Penguin 2.1
- December 17th: unnannouced Panda refresh
2014
- February 6th: 3rd Top Heavy Page Layout algo update
- May 17th weekend: Spammy Query algo update 2.0 which impacted 0.3% of queries to a noticeable degree (the original version launched)
- May 20th: Panda 4.0 which impacted 7.5% of English language queries to a noticeable degree. the original Panda impacted 11.8% of English language queries to a noticeable degree.
- June 12th: Spammy Query algo update 3.0 was claimed to impact spammy sites whereas the prior version was claimed to focus more on spammy queries.
- June 22nd: unannounced Panda update
- July 24th: Pigeon local search update
- August 27th / 28th: unannounced Panda update
- September 25th through first week of October, though some saw movement on the 21st: Panda 4.1 update impacting 3 to 5% of search queries.
- October 17th: Penguin 3.0, though there was an overlapping Panda update used to mask it. The refresh affected under 1% of US English queries.
- November 27th: continuation of Penguin 3, with more recoveries.
- December 18th: Pigeon update rolled out to Canada, Australia & the UK.
2015
- January 24th: David Naylor believes Google may have rolled out a mobile-friendly related ranking factor then.
- March 16th: on March 16th Brian White announced Google would soon roll out a doorway page update.
- Mobile Friendly Design Update April 21st: Google announced on February 26th that Google will launch a mobile-ranking update on April 21st. The algorithm will be applied in real-time & have a page-level impact. While the 21st was referenced as the day of the update, many people did not see any significant changes until a day or two later & the update was scheduled to roll out over the following week. For as heavily hyped as the update was, it has fairly minimal impact on search traffic.
- April 28th & May 3rd: unnanounced update, which some people thought was associated with Panda. Google claimed there was "no update" but informed SEOs looking at the SERPs noticed a significant change. Glenn Gabe & HubPages' Paul Edmondson wrote about the change, which Google later confirmed as a "quality" update. This update was also called Phantom 2.
I found an example of a traditional Panda hit. And it's HUGE. ~85% decrease, starting on 4/28. Holy smokes #seo pic.twitter.com/RaLPNmRv3o
— Glenn Gabe (@glenngabe) May 4, 2015 - June 16th: an update appeared to extend some of the impacts of query deserves freshness (QDF)
- July 19th - ?: Panda 4.2 is slowly rolling out over the course of many months, with some biweekly data refreshes lasting through September.
- September 16th: Phantom/Quality update 3
- ~ Octover 5th: Google updated their display of search results for some keywords commonly targeted by hackers to show fewer organic results on the first page.
- October 26: Rankbrain announced as a machine learning improvement to hummingbird. In early 2022 Google offered a small primer on RankBrain, neural matching, BERT and MUM here.
- November 19th: Phantom 3 (see here or here)
2016
- January ~ 8th - 11th: update to the core ranking algorithm
- Feb 23: Google shifted from showing up to 8 right rail textads & up to 3 top ad units to showing no right rail ads (unless they are shopping ads) and showing up to 4 ad units at the top of the search results. Around the same time Google announced they were shutting down their Google Compare / Google Advisor vertical shopping comparison service which operated in markets like credit cards, mortgage rates and insurance. A couple days later Google added more whitespace between the search results to further push the organic results below the fold.
- March 3, 14 & 21: adjustments which appear to be related to phantom updates (thus related to search quality / Panda).
- May 11: mobile friendly update 2.0 now live.
- June: Phantom/Quality update #4
- July 26: broad roll out of Google AdWords expanded text ads, which further displace organic results by pushing them below the fold on more devices.
- September 1st: local update
- September 2 (ongoing throughout month): likely a quality update, either new singal reweighting or a quite major data refresh. (I believe this was them testing Penguin 4).
- September 20: Google AMP live in mobile search results in categories beyond news.
- September 23: Penguin 4.0 live. real-time updates & more granular impacts rather than sitewide hits.
@randfish Incredibly important point is the devaluing of links & not "penalization". That's huge. Knocks negative SEO out. @dannysullivan
— Glenn Gabe (@glenngabe) September 23, 2016 - November 10 & 18: tested update which was rolled back
2017
- January 10: mobile interstitial usage ranking demotion
- February 1: unannounced update which hit some sites using low quality link sources, such as private blog networks (PBNs)
- February 3: Japanese content quality-related update
- February 7: unnamed update, likely associated with Panda & some of the AI aspects of their relevancy scoring for the quality of user experience
- March 7th - 9th: update Fred
- April 25th: Project Owl added direct user feedback to featured snippets & search suggestions, while the barrier to entry in order to appear in featured snippets was also raised
- May 17th: another quality-based update
- June 20th: Google launched their Jobs search feature in their web search results
- June 25th: quality update
- July 26th: Google dropped Google Instant search results
- August 14th & 19th: another Google quality update
- August 22: update to local result filtering
- August 30th: Featured snippets switched to leveraging AMP on mobile devices
- December 15th: many official celebrity sites saw their rankings fall. Many versions of the Google Remote Rater guidelines instructed raters to put a "vital" rating on official websites, so the idea of seeing a celebrity's official website drop from #1 to #9 for their own name is quite significant. The month of December also had other minor updates in the early to mid parts of the month. In addition, on December 26th many people were sent manual penalty notifications for unnatural link profiles. Overall this was likely the most volatile December in history, breaking from Google's alleged policy of trying to keep the ecosystem fairly stable during the holidays & throughout the late holiday shopping season.
2018
- February 15: Chrome to begin ad blocking on sites it deems to have a poor Ad Experience based on the Coalition for Better Ads standards.
Chrome will remove all ads from sites that have a “failing” status in the Ad Experience Report for more than 30 days. Assessment of participating companies’ compliance conducted in connection with the Program will be based on measureable, empirical thresholds that establish the frequency of display of ad experiences that do not comply with the Standards. In the initial phase of the Program’s operation, the threshold for non-compliance for web sites will be measured according to the following percentages of page views assessed:
- 7.5% in the first two months following the Effective Date of the Program
- 5% in the ensuing four months
- 2.5% in the months thereafter
- Early March: Core algo update, focused on search quality. The update was rolled out over time in multiple waves, with significant volatility in the results on the 7th & 14th, followed by another wave of volatility on the 18th & 23rd.
Each day, Google usually releases one or more changes designed to improve our results. Some are focused around specific improvements. Some are broad changes. Last week, we released a broad core algorithm update. We do these routinely several times per year....
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) March 12, 2018 - March 26: Google began broadly rolling out mobile-first indexing, which uses the mobile version of a page as the canonical version.
- April 16: Core ranking algo updated once more. Glenn Gabe wrote about how the March & April updates tie together.
On Monday, we released a broad core algorithm update, as we routinely do throughout the year. For background and advice about these, see our tweet from last month: https://t.co/uPlEdSu6xp
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) April 20, 2018 - July 9th: mobile page speed became a ranking factor for search (previously the speed signal was focused on desktop searches)
- July 24th: pages not using HTTPS are marked "not secure" in Chrome 68.
- August 1st - 7th: broad core update which had a significant impact on sites in the health category & some other your money your life (YMYL) categories.
This week we released a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. Our guidance about such updates remains the same as in March, as we covered here: https://t.co/uPlEdSLHoX
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) August 1, 2018 - August 22nd: yet another update
- September 18th - 20th: elevated volatility
- September 24th: for their 20th anniversary Google announced improvements to visual search, adding a news feed to the default search homepage, grouping related searches in journeys & more layers to the knowledge graph. Some branded search queries now include classification groups at the bottom of the search results for things like storage companies, computer manufacturers, multinational corporations, etc.
- September 26th - 27th: elevated volatility
- October 31 - November 7th: unnamed update
2019
- February 27: increased volatility shown on multiple rank trackers
- March 12: Google announced a broad algorithm update, which was significant enough that WebmasterWorld founder Brett Tabke dubbed it Florida 2.0, though it is unrelated to the original Florida update from 2003. So far it appears some sites with eggregious anchor text repetition were hit hard, while the apparent anchor text adjustment also coincided with a rescoring of other search quality-based algorithms. Many sites which were hit on the August 1st update in 2018 recovered according to many of the rank monitoring tools. Google also stated the update was not associated with any major change in their neural matching technology: “Neural matching has been part of our core ranking system for over half-a-year. None of the core updates we have confirmed coincided with some new use of neural matching,” the company said.
This week, we released a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. Our guidance about such updates remains as we’ve covered before. Please see these tweets for more about that:https://t.co/uPlEdSLHoXhttps://t.co/tmfQkhdjPL
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) March 13, 2019 - April 7: Major reverberation on the above Florida 2.0 update. It appears Google is mixing in showing results for related midtail concepts on a core industry search term & they are also in some cases pushing more aggressively on doing internal site-level searches to rank a more relevant internal page for a query where they homepage might have ranked in the past. Google also has some issues with many pages being dropped from their search index.
We're aware of indexing issues that impacted some sites beginning on Friday. We believe the issues are mostly resolved and don't require any special efforts on the part of site owners. We'll provide another update when the issues are considered fully resolved.
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) April 7, 2019 - April 27: minor update, perhaps a continuation or rescoring of the above update which began on March 12th.
- June 3 - 8: another major core update. the Daily Mail's Mail Online lost half their organic search traffic & 90% of their Google news feed traffic
Tomorrow, we are releasing a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. It is called the June 2019 Core Update. Our guidance about such updates remains as we’ve covered before. Please see this tweet for more about that:https://t.co/tmfQkhdjPL
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 2, 2019 - June 4 - 6: update to promote increased result diversity by typically limiting the number of results that can appear from any individual domain (inclusive of subdomains) to 2 results in cases where the user intent is not navigational to that particular site
This site diversity change means that you usually won't see more than two listings from the same site in our top results. However, we may still show more than two in cases where our systems determine it’s especially relevant to do so for a particular search….
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 6, 2019 - July 11-13: unannounced update with a further spike in ranking volatility on the 18th
- September 10th: Google announced they would treat rel="nofollow" as a hint versus a directive & also launched rel="ugc" for user generated content & rel="sponsored" for links which are based on financial compensation.
- September 24th: another core update which seemed to have increased weight on link authority relative to the weight placed on engagement for a particular keyword.
- September 24th: Google announced a new meta tag which limits snippet performance on featured snippets. This will go live in the middle of October & these will operate as directives versus hints.
- individual options
- "nosnippet" = if featured snippets can be used
- "max-snippet:[number]" = how many characters can be shown in a featured
- "max-video-preview:[number]" = how many seconds of an animation can be shown in a preview
- "max-image-preview:[setting]" none, standard or large = limit size of preview images shown. This can also be used in AMP.
- examples
- <meta name="robots" content="max-snippet:75, max-image-preview:standard, max-video-preview:10">
- <meta name="robots" content="nosnippet">
- In addition, there is a new data-nosnippet attribute which can be applied to specific spam, div & section elements within a page to prevent that portion of the page from appearing in search snippets.
- example usage <p><span data-nosnippet>Peanut butter</span> is the most delicious food. Period.</p>
- The new granular snippet controls are a core plank in Google's efforts to play hardball with publishers & evade compulsory copyright fees to European news publishers as the Article 15 copyright directive goes into effect in October. Much like how efficient PPC markets have marketers bidding against one another to see who can hand Google more money, French news publishers will either appear with little to no supplemental information (& thus get few search clicks), apply for a broad-based exemption to show full listings, or use the granular controls to set how much of their content appears in search. Those who opt to show more information will likely garner better user engagement, more search traffic, more influence & higher rankings.
- individual options
- October 22nd to 25th: Google rolled out BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), a Rankbrain like neural network-based technique for natural language processing to better understand the user intent of search queries & rank documents which match the searcher's intent. A before and after example they gave was a person searching for travel information to the United States from Brazil may have previously seen an article about a US person visiting Brazil but will now get the result directionally correct, returning documents about how Brazillians can visit the United States.
by applying BERT models to both ranking and featured snippets in Search, we’re able to do a much better job helping you find useful information. In fact, when it comes to ranking results, BERT will help Search better understand one in 10 searches in the U.S. in English, and we’ll bring this to more languages and locales over time.
Dawn Anderson did a deep dive review on the technology associated with BERT here. Google's Pandu Nayak described the ranking signal update as "the single biggest change we’ve had in the last five years — and one of the biggest from the beginning." - October 30th - November 1 & November 9th: More unannounced updates, including a later confirmed update which used neural matching in local search.
- December 17th - December 19th: Another unannounced update, which appeared to have increased the weighting on link equity.
2020
- January 13 - January 16: Another broad core update
Later today, we are releasing a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. It is called the January 2020 Core Update. Our guidance about such updates remains as we’ve covered before. Please see this blog post for more about that:https://t.co/e5ZQUA3RC6
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) January 13, 2020
When Google rolled out the above update they shifted their default desktop search results to using favicons like they do by default on mobile devices
Last year, our search results on mobile gained a new look. That’s now rolling out to desktop results this week, presenting site domain names and brand icons prominently, along with a bolded “Ad” label for ads. Here’s a mockup: pic.twitter.com/aM9UAbSKtv
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) January 13, 2020 - January 22nd: Google announces de-dupliation between organic search results & the featured snippet. Featured snippets now count as one of ten organic listings & if a page appears in the featured snippet spot it won't be repeated in the remaining organic results.
If a web page listing is elevated into the featured snippet position, we no longer repeat the listing in the search results. This declutters the results & helps users locate relevant information more easily. Featured snippets count as one of the ten web page listings we show.
— Danny Sullivan (@dannysullivan) January 22, 2020
Some advertisers saw an immediate jump in thier ad CTR after the new search layout was announced. In response to broader web criticism from sites like TheVerge Google stated they would test other layouts.
Our experimenting will begin today. Over the coming weeks, while we test, some might not see favicons while some might see them in different placements as we look to bring a modern look to desktop….
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) January 24, 2020 - February 7-8th: unannounced update
- March 1st: Link rel="nofollow" attribute becomes a hint versus a directive for ranking purposes.
- March 2nd: Update appears to have granularized some cross-country localization
This update (happened yesterday?) caused “similar languages” to be far more likely to rank in counties where the specific* language isn’t spoken, but is understood. For example, Czech sites are crowding many Slovak SERPs now, whereas before they weren’t. @rustybrick
— SEOwner (@tehseowner) March 3, 2020 - March 23rd: Unnanounced update which either seemed to place more weight on link diversity or lower the dampening on links relative to other ranking signals.
- May 4 - May 18: Google update
Later today, we are releasing a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. It is called the May 2020 Core Update. Our guidance about such updates remains as we’ve covered before. Please see this blog post for more about that:https://t.co/e5ZQUAlt0G
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) May 4, 2020 - June 3rd: Google announced they now redirect some featured snippet clicks to the relevant section of the associated web page
As we have done with AMP pages since December 2018, clicking on a featured snippet now takes users to the exact text highlighted for HTML pages, when we can confidently determine where the text is, for browsers that support the underlying technology….
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 3, 2020
This change could have a significant impact on the earning power of some rankings:"With this, searchers may skip down past ads and/or call to actions to jump directly to the relevant content. SEOs should take measures to track if your site is doing this in Google search, and possibly replace your ads/call to actions in a more appropriate location."
Publishers can opt out of appearing in featured snippets by using the nosnippet tag. - August 10th: Google rolled out a dumpster fire core algorithm update they quickly reverted and referred to as a glitch in their indexing system
I don't have all the details yet, but it seems like this was a glitch on our side and has been fixed in the meantime.
— John (@JohnMu) August 11, 2020
If someone could fix the other 2020-issues, that would be great.
On Monday we detected an issue with our indexing systems that affected Google search results. Once the issue was identified, it was promptly fixed by our Site Reliability Engineers and by now it has been mitigated.
— Google Webmasters (@googlewmc) August 11, 2020
Thank you for your patience!
The indexing system, Caffeine, does multiple things:
— Gary Illyes (@methode) August 11, 2020
1. ingests fetchlogs,
2. renders and converts fetched data,
3. extracts links, meta and structured data,
4. extracts and computes some signals,
5. schedules new crawls,
6. and builds the index that is pushed to serving.
If something goes wrong with most of the things that it's supposed to do, that will show downstream in some way. If scheduling goes awry, crawling may slow down. If rendering goes wrong, we may misunderstand the pages. If index building goes bad, ranking & serving may be affected
— Gary Illyes (@methode) August 11, 2020
We still had the index (the index db), but something was wrong with it, because of how it was built by Caffeine. That's why we said it was an indexing issue, which manifested as a ranking issue externally.
— Gary Illyes (@methode) August 11, 2020
Also, we can rebuild the whole serving index (db) within hours, yes. - October 1st: Google announced they have 2 indexing issues they are looking to resolve around canonicalization and mobile indexing.
We are currently working to resolve two separate indexing issues that have impacted some URLs. One is with mobile-indexing. The other is with canonicalization, how we detect and handle duplicate content. In either case, pages might not be indexed....
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) October 1, 2020 - October 15th: Google's Search On virtual event with Prabhakar Raghavan mentioned the following search information and organic search relevancy advancements.
- 15% of daily search queries are still unique
- 10% of search queries are misspelled
- Google BERT is now used on almost every English language search query.
- Using neural nets enables them to provide listings of diverse subtopics when a person searches on a broad topic like home exercise equipment: "we can now understand relevant subtopics, such as budget equipment, premium picks, or small space ideas, and show a wider range of content for you on the search results page."
- Google will soon launch a feature called passage-based indexing which focuses on identifying individual passages in a web page and ranking them based on their relevancy. This feature will...
- roll out later this year
- impact about 7% of Google search queries off the start
- better rank relevant key passages on larger pages even if the page itself is about a broader, different or less relevant topic.
- allows them to search across key segments of video content and direct searcher attention to what they believe are the most relevant segments.
- The video outlining these updates is below
- ~ November 15: subtopic rank - Google adjusted their search relevancy ranking algorithms on core terms to include results for subtopics, which they suggested impacted 7% of search results.

- December 3 - December 16: Google announced a major broad search quality update. On November 9th some sites which were algorithmically suppressed had their ability to rank improve, so presumably for many of those sites Google has now collected enough engagement metrics to re-adjust their rankings based on end user enagement data. In a subsequent tweet they stated the update would take 1 to 2 weeks to fully roll out, then in a third Tweet said the update was complete on December 16th.
Later today, we are releasing a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. It is called the December 2020 Core Update. Our guidance about such updates remains as we’ve covered before. Please see this blog post for more about that:https://t.co/e5ZQUAlt0G
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) December 3, 2020
2021
- February 10: Passage ranking was rolled out in the English language in the United States. Google anticipates when the change is rolled out globally it will impact roughly 7% of search queries. This feature allows sections of longer & deeper pages on broader topics to rank higher for search queries relevant to a specific section of the page. Think of it as being the sort of opposite of the hyper-focused stub page eHow or Mahalo type sites were known for, where a section of an in-depth research paper can now better rank for a specific topic covered in a section within it.
Update: passage ranking launched yesterday afternoon Pacific Time for queries in the US in English. It will come for more countries in English in the near future, then to other countries and languages after that. We'll update this thread as those further launches happen.
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) February 11, 2021 - February 16: unconfirmed algorithm update
- Mobile-first indexing for all sites: on July 21, 2020 Google's Yingxi Wu announced Google was pushing back the mobile-first indexing date from September 2020 to March 2021.
- April 8 - 22: Ecommerce reviews update. Google recently rolled out a parasitic spam offering focusing on the most widely searched for products. To make room for promoting their spam they launched a product reivew update which nuked the rankings of some smaller affiliates so the traffic hit other big ecommerce players would see on Google's inorganic promotion of their thin spam layer would be partly offset.
- User Experience Signals: On May 28, 2020 Google search ecosystem director of engineering Sowmya Subramanian announced Google will incorporate user experience directly into rankings in 2021. The post mentioned...
- they would give webmasters at least a 6 month lead time before rolling out the new ranking algorithm
- AMP would no longer be required to appear in Top Stories
- this update will incorporate existing metrics (mobile friendly design, safe browsing, using HTTPS, no intrustive interstitial ads) along with new metrics from Core Web Vitals measuring loaing speed, interactivity and visual stability, as shown in the following graphic
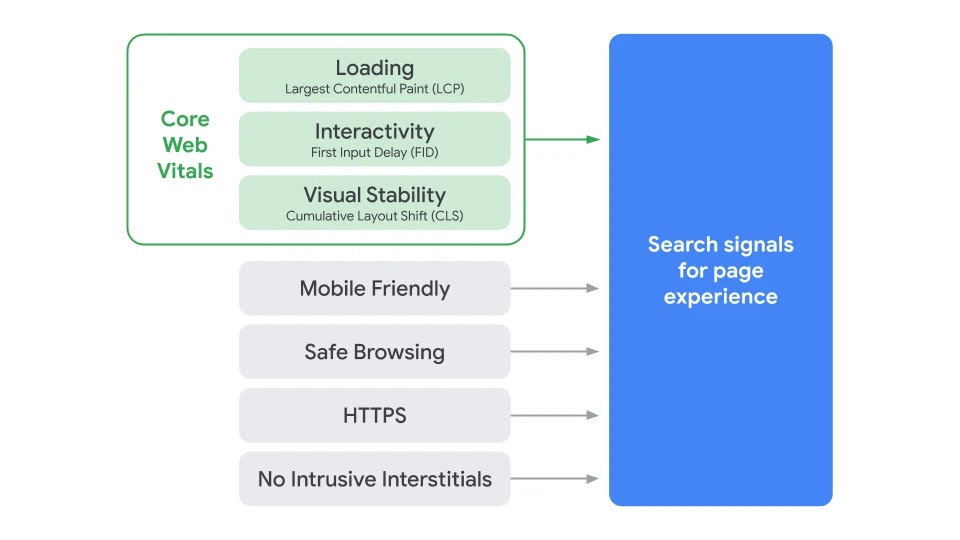
- Here is a great article about layout shifts from webfonts.
- June 2 - 12: Broad core update rolled out. Update analysis available on SEL. The update concluded on June 12th.
The June 2021 Core Update is now rolling out live. As is typical with these updates, it will typically take about one to two weeks to fully roll out.
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 2, 2021 - June 15 - September 2: Google began a slow roll out of page experiences update, which is anticipated to last through August.
- June 23: Google rolled out a spam update which was completed on the same day it rolled out. They also promised a second spam update the subsequent week.
As part of our regular work to improve results, we've released a spam update to our systems. You can learn more about our efforts to fight spam in this post:https://t.co/piCLhbZPkH
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 23, 2021
And this video below:https://t.co/xMYWm4HPze pic.twitter.com/83IL0EB9Lm - June 28: Second part of the spam update.
The second part of our spam update has has begun today, and it will also conclude later today, unless we share otherwise.
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 28, 2021 - July 1 - July 12: July core update timed perfectly for a long holiday weekend so that many people who are not penalized but invested heavily in SEO think they were penalized over the weekend while traffic is lower from the holiday weekend and nobody is at work.
The July 2021 Core Update, previously announced, is now rolling out:https://t.co/6Xs77WDsur
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) July 1, 2021
These typically take 1-2 weeks to finish. Our guidance about such updates is here:https://t.co/e5ZQUA3RC6
Here’s more on how we improve search through updates:https://t.co/IBmInwGOiX - July 23: Google rolled out an algorithm update which penalized ... erm ... aggressive link building. They only announced the start of that update on the 26th as the "link spam update" & stated the update will roll out over 2 weeks. In the post announcing the update they took a dim view of unlabeled affiliate links (suggesting the use of rel="sponsored") & guest posting on other websites for link building (hinting rel="nofollow" should be used). On August 24 Google announced the update was complete.
- August 17: Google started using on-page headings and internal anchor text more frequently when they decide to rewrite page titles shown in the search result snippets.
- October 14: Continuous scrolling of the SERPs on mobile devices.
- November 3 - 11: Google spam update, which concluded on November 11th.
As part of our regular work to improve results, we've released a spam update to our systems. This November 2021 spam update should be fully rolled out within a week. We encourage sites to follow our best practices for Search: https://t.co/jK3ArQmTqT
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) November 3, 2021 - November 17 - 30: core updatem which ended on the 30th
Later today, we are releasing a broad core update, as we do several times per year. It is called the November 2021 Core Update. Our guidance about such updates is here:https://t.co/0LAL28ueDq
— Google Search Central (@googlesearchc) November 17, 2021 - December 1 - 21: product review update
- ...
2022
- February 22 - March 3: Desktop page experience update.
- March 23: Google rolled out their third major product reviews update in the past 12 months. The update will happen over a couple weeks.
- May 25 - June 9: Core update begins roll out.
- July 27 - August 2: English-language product review update
- August 11: Google announced an update which lowered how frequently they showed featured snippets when a correct answer was unclear / less certain, along with other "information literacy" aspects.
- August 25 - September 9: On August 19th Google announced a helpful content update which would begin over the next week and last for roughly 2 weeks. On August 25th the announced the update had started rolling out that morning.
- The update is based on a sitewide classifier which demotes sites which are perceived to have volumes of unhelpful content published.
- The classifier runs continuously & the flag may take months to disappear from a site which is flagged for demotion. If Google sees all of the problem has been cleaned up it will still be an additional couple months from that date before the penalty is cleared.
- The update is expected to roll out of the course of a couple weeks for the English language globally, and then apply to other languages later.
- Barry suggested the update would be large & could likely be grouped with Florida, Panda & Penguin in terms of impact.
- The update ended on September 9th & had a fairly weak impact compared to most prior major announced updates. In terms of impact it was nothing like the big updates mentioned above.
- September 12 - September 26: September 2022 Core Google update rolled out.
- September 20 - September 26: September 2022 product reviews update rolled out.
- October 19: October 2022 spam update began rolling out.
- December 5: December 2022 helpful content update rollout began. Completed on January 12, 2023.
The Dec. 2022 helpful content update was released Dec. 5, starting to become more visible today & will take about two weeks to fully roll out. It improves our classifier & works across content globally in all languages. Our help page explains more: https://t.co/MS7hbcBTsp
— Google Search Central (@googlesearchc) December 6, 2022 - December 14: December 2022 link spam update using SpamBrain. Completed on January 12, 2023.
2023
- AI Search (various dates)
- On February 7 Microsoft announced the new Bing, which incorporated A.I. features into their search engine & the Microsoft Edge web browser.
- On February 6 Google pre-announced their A.I. search tool Bard (to try to steal Microsoft's thunder on the PR front).
- On April 16th the New York Times published an article suggesting Samsung considered switching to Bing as their default search engine. The article stated Google is rebuilding a new A.I. focused search engine, while another team of 160 workers is adding A.I. features to Google's existing search engine in a project codenamed Magi. The new features will initially be available in the United Sates to a subset of users in May.
- In September Google started giving some startups access to their Open AI competitor Gemini.
- February 21- March 7: February 2023 product reviews update
- March 15 - 28: March 2023 core update
- August 23 - September 7: August 2023 core update
- September 14 - 28: September 2023 helpful content update
- October 4 - 19: October 2023spam update "This spam update aims to clean up several types of spam that our community members reported in Turkish, Vietnamese, Indonesian, Hindi, Chinese, and other languages. We expect this to reduce the visible spam in search results, particularly when it comes to cloaking, hacked, auto-generated, and scraped spam."
- October 5 - 19: October 2023 core search update
- November 2 - ~ 15: November 2023 core search update
2024
- March 5: Google announced they were complying with the European Union's Digital Markets Act. As part of that post they mentioned: "changes to our Search results may send more traffic to large intermediaries and aggregators, and less traffic to direct suppliers like hotels, airlines, merchants and restaurants."
- March 5 ~ April 19 + May 6: Update sandwich
consisting of the following elements
- March 2024 core update was concluded on April 19, though Google did not announce it until April 24.
- When they announced the update was complete they provided a ranking update feedback form that they stated would be live until May 31.
- The ranking feedback form requested search query, what page you think should appear in the top 10 results, and any additional optional details along with a bullet point selection between the following options (where a user must select one):
- My page no longer ranks in the top 10 results for this query.
- My page is in the top 10 results but no longer as high as it was.
- Someone else's page should be ranking in the top results for this query.
- All or most of the top results are generally poor for this query.
- A few or some of the top results are poor for this query.
- It's a general issue / something else.
- Helpful content update - they also published a companion clarifying FAQ page mentioning there are many signals & mentioned helpful content is now becoming core algorithm, so going forward there won't be separate helpful content updates
- Spam update - the initial portion of the spam update was completed March 20, though some new policies will begin enforcement on May 5 to give publishers time to adjust their practices
- Expired domain abuse - uses an example of placing a casino site on a prior trusted domain that expired
- Scaled content abuse - many pages created with the intent of manipulating search results (applies based on perceived intent, if one does it manually or using AI content generation)
- Site reputation abuse - the "goog enough" issue highlighted on BlindFiveYearOld, where newspapers or other trusted sites syndicate content for a third party & leverage the core domain trust to rank content where the main publication is not exercising editorial control.
- Google clarified syndicating press releases or normal news syndication deals are not a problem, but syndicating coupons or similar with no editorial oversight is a problem.
- Far off topic content that is not published in an obvious "advertorial" format is also a problem.
- Google stated some of the new site abuse policies will begin enforcement on May 5, 2024.
- On Twitter Danny Sullivan announced enforcement of the site reputation abuse policy began on May 6, 2024.
- Many sites which were engaging in the activity deleted the associated sections of their site or blocked them from indexing using robots.txt.
- March 2024 core update was concluded on April 19, though Google did not announce it until April 24.
- May 14: Google announced they were rolling out AI Overviews on search results inside the United States for all searchers, and that the feature would roll out globally by the end of the year. They also showcased multi-step advanced features launching soon, which will allow processing of more complex search queries.
- June 20 - June 27: June 2024 spam update, with a ~ 1 week roll out period. It was a broad & general spam update, and did not focus specifically / exclusively on link spam.
- June 25: Google dropped continuous scroll from desktop search results & stated they will do the same on mobile in the coming months.
- July 5: Google will no longer crawl & index web pages that do not render on Googlebot Smartphone.
- August 15 - September 3: August 2024 core update. The update claimed to have done some work on solving some of the "bury small websites by driving their owners toward insolvency" problem that Google has been working hard on over the past decade or so. The odds of that promise being met as a high priority in the age of AI publishing are quite low. Some sites which were hit by the "Helpful Content Updates" saw recoveries early in this update cycle, though only few saw actual full recoveries. Most gains were off a low base. If you lose 90% of your traffic and then double you are still off 80%.
- November 11 - December 5: November 2024 core update.
- November 19th - 20th: a wave of manual penalties went out for parasite hosting reputation abuse on trusted sites, where folders of sites were deindexed after working with entities like Three Ships to add affiliate reviews on trusted news sites & magazine sites. In early December Google also added an FAQ section to their reputation abuse policies.
Huge heads-up! The manual actions for 'Site reputation abuse' have already started going out based on the policy update. Jason Kilgore first pinged me on LinkedIn that Forbes Advisor is not ranking for what it once was (not even for the query 'Forbes Advisor')... and it looks… pic.twitter.com/YqSTeCFyXm
— Glenn Gabe (@glenngabe) November 20, 2024 - December 5: Google added a statement to the bottom of the SERP to indicate if results are personalized & a link to turn personalization off by appending &pws=0 to the URL. If you repeatedly search for a query and click on a particular result then that result may rank higher. If you repeatedly search for a query without clicking on anything then the ad load shown on the page will likely be lower so that the non-clickers have less impact on the ad auctions.
- December 12 - 18: December 2024 core update.
- December 19 - 26: December 2024 spam update.
2025
- March 5: Google launched AI Mode in Google Search.
- March 13 - 27: Google launched March 2025 core update.
- March 26: Google rolled out AI overviews across much of Europe, including Austria, Belgium, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Poland, Portugal, Spain, and Switzerland. Google also shared many ways they are using AI in the travel industry, including autogenerating trip ideas & multimodal AI search advances. Google regularly cites their own search results as sources in the AI-generated listings to boost search query volume, and is testing sending some searches directly to AI-mode results without traditional organic search results. Google published guidelines for ensuring content performs well in Google's AI search experiences. Google's VP of search Elizabeth Reid published a blog post about expanding AI overviews, along with some of the logic that goes into when they are triggered.
- April 15: Google announced they will do away with using CCTLDs to handle local searches, and will instead redirect all searchers to Google.com. They stated the change would happen gradually over the coming months.
- June 30 - July 17: Google announced the June 2025 core update.
- August 26 - September: Google announced the August 2025 spam update, which will roll out over the subsequent 2 weeks.
- ...
- The End of History and the Last Man
Other Algorithm Update Lists
Here are a few third party algorithm update lists & tools...
- Google - the borg's official list, which starts in 2020 and runs up to present
- Bronco.co.uk: Google Update Calendar
- VisualSoft - an interactive infographic going back to 2003
- Moz - a fairly comprehensive listing
- RankRanger - similar to the Moz page
- Sistrix - a more limited timeline
- Maria Haynes
- Panguin Tool - Google Analytics overlay. there's another quick penalty analysis tool here
- Dave Davies put together a 3 part retrospective on the history of search via Matt Cutts: 2000-2005, 2006-2010, & 2011-2014
- Google's guide to monoitoring and debugging search ranking issues including algorithm update-related issues.
- A guide to Google Search ranking systems - Google detailed many of their current ranking subroutines and past ones which have been retired.
- Active
- BERT - an AI system for understanding the intent behind various word combinations
- Crisis Information systems - provides SOS alerts and access to support systems for individuals
- Deduplication system - compares the content of top ranking pages & filters out near identical repeats
- Exact match domain system - a ranking routine which aims to prevent an exactly matching domain from counting too much toward ranking in general web search
- Freshness system - boosts the rankings for fresh results when there are signals a query deserves freshness. such signals include a spike in search volume or many news publishers covering a topic.
- Helpful content system - boosts ranking of content which is believed to have been written by people for people with intent of being helpful, rather than an entity using automation to chase search traffic
- Link analysis system and PageRank - analyzing the quality, quantity, and anchor text of links into a site & into a particular page
- Local news systems - surfaces local news
- MUM - AI used to improve feature snippet callouts & improve COVID-19 vacine information searches
- Neural matching - AI system used to understand representations of concepts in search queries and web pages, matching them together where there is a strong fit.
- Original content systems - systems which aim to rank original reporting and other original content above other publishers who cite or rehash original reporting.
- Removal-based demotion system - remove content deemed illegal including non-consentual explicit issues and DMCA takedowns. repeatedy removals can lead to sitewide demotions or even indexing issues.
- Page experience system - gives rank preference toward pages with a good user experience. includes signals like mobile friendly layout, lack of intrusive interstitial ads, and pages which are served quickly and over HTTPS.
- Passage ranking system - AI system used to rank sections or "passages" within a broader web page.
- Product reviews system - aims to better reward sites offering in-depth original research and reviews by experts & enthusiasts.
- RankBrain - AI system which relates words with concepts to return relevant results even if those lack the exact words used in a search.
- Reliable information systems - ranking routines which aim to surface authoritative pages and demote low-quality content.
- Site diversity system - limits the number of results from any site to 2, unless the search query is deemed to be navigational or there is some other reason to rank more results from a singular domain.
- Spam detection systems - SpamBrain and other spam detection systems which work to demote content and behaviors deemed to violate Google's spam policies.
- Retired
- Hummingbird - ranking system improvement launched in August 2013.
- Mobile-friendly - gave preference to content formated well on mobile devices. associated signals baked into page experience system.
- Page speed - announced in 2018. associated signals baked into page experience system.
- Panda - announced in 2011 to fight low quality content & folded into core in 2015.
- Penguin - launched in 2012 to fight link spam & folded into core in 2016.
- Secure site - announced in 2014. associated signals baked into page expereince system.
- Active
Search Flux Monitors
These are tools which use a seed set of keywords and compare today's search results against yesterday's results & then compare how much the recent change has been against the typical daily churn.
- Mozcast - one of the more popular flux monitor tools. Contains metrics for SERP diversity and domain name related measurements. They also show some of the current layout shifts being tested here.
- AdvancedWebRanking - overlay launched in 2014. offers US, UK & DE information. They also offer a CTR curve where you can select the month to see how CTRs have changed over time.
- SEMrush Sensor
- Serpmetrics
- RankRanger has both a SERP flux tracker and a SERP feature tracker
- Algaroo
- Ayima Pulse
- Accuranker Grump
- SERP.watch
- SEOWetter.de
- SimilarWeb SERP Seismonitor
- cognitiveSEO SIGNALS





